Covid-19 briefing
Powered by
Download GlobalData’s Covid-19 Executive Briefing report
- ECONOMIC IMPACT -
Latest update: 15 September
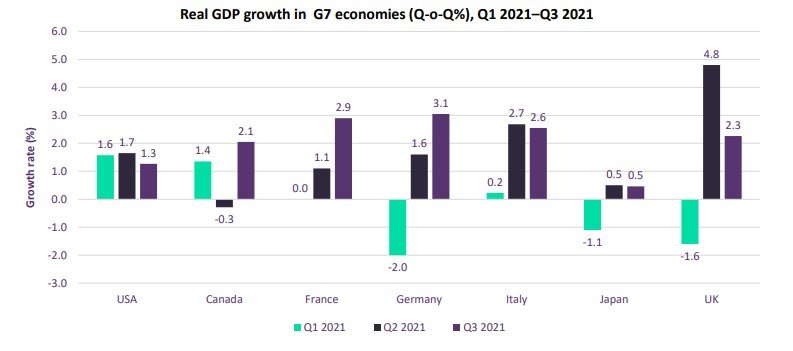
The unemployment rate in OECD nations stood at 6.2% in July 2021, down from 6.4% in June 2021. The unemployment rate among G7 nations also declined from 5.5% in June 2021 to 5.2% in July 2021.
Economic growth in Argentina is forecasted at 7.2% in 2021, an improvement from the August forecast of 6.8% growth, according to a Central Bank of Argentina poll.
5.7%
World economic growth is projected at 5.7% in 2021 and at 4.5% in 2022, according to research by HIS Markit.
217 million
The virus has now spread to 198 countries with more than 217 million confirmed cases and more than 4.5 million deaths.
- SECTOR IMPACT: CONSTRUCTION
Latest update: 3 September
Despite the huge stimulus packages, sharp cuts in interest rates and other unprecedented policy measures across all major markets, the construction industry is likely to be subdued beyond the immediate period of lockdowns and other containment measures.
Generally, the construction industry will be heavily affected by the expected widespread disruption to economic activity and a likely drop in investment, which could lead to planned projects being delayed or cancelled.
Commercial: significant negative impact
Commercial construction is likely to be the hardest hit in 2020, with sectors such as retail, leisure and hospitality already suffering from the decline in trade, travel and consumer and business confidence.
Residential: significant negative impact
The residential sector will struggle as unemployment rises, despite low interest rates and direct government support. There is a high risk that a considerable proportion of early-stage projects in the sector will be cancelled or delayed.
Industrial: significant negative impact
The industrial construction sector is most at risk from the severe drop in economic activity. Immediate priorities for manufacturers will be to stay afloat and rebuild core operations, rather than invest in new premises or capacity.
Energy & utilities: moderate negative impact
Spending on energy and utility projects will be severely impacted by global supply chain disruptions and low oil prices. However, governments and public authorities will likely advance spending on power and utilities projects as soon as normality returns.
Institutional: significant positive impact
Governments are strengthening their healthcare infrastructure and the number of new hospital projects is rising sharply. This investment is helping to support the institutional building sector.
Infrastructure: moderate negative impact
Infrastructure projects will be a priority for government investment as soon as normality returns. With interest rates at record lows, borrowing costs will be at a minimum, but success will depend in part on the financial standing of governments post-Covid-19.